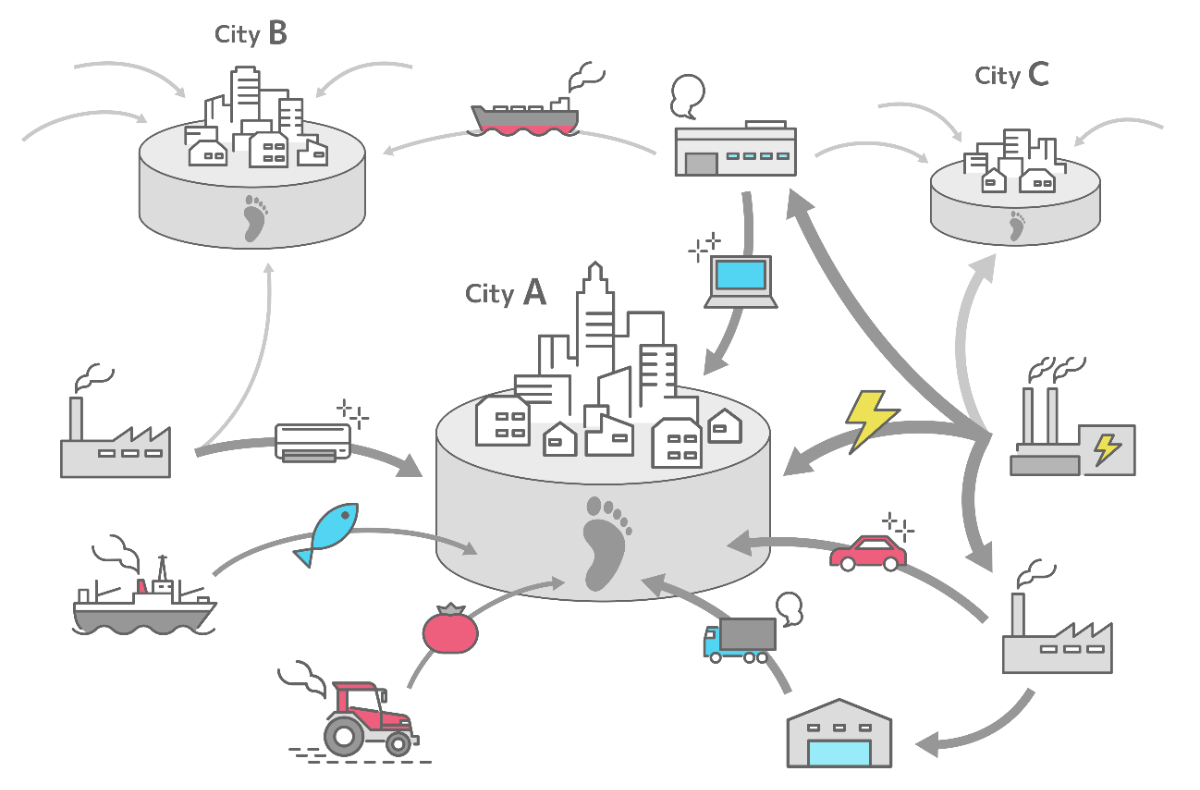
Consumption-based CO2 emissions of cities
Consumption-based emissions refer to the emissions from the process of producing the products and services consumed by city residents, rather than the actual emissions at that location. For example, even if a city has a large thermal power plant that emits a large amount of CO2 emissions, the electricity is still mainly used in other cities. In consumption-based accounting, the CO2 emissions from the thermal power plant are allocated to the city that consumes the electricity.
In order to reduce consumption-based CO2 emissions, it is possible to reduce CO2 emissions by changing the consumption behavior of the residents living in that city, rather than by encouraging the companies in that city to reduce their CO2 emissions. For example, cities can reduce CO2 emissions on a consumption basis by encouraging residents to use public transportation instead of private cars, reduce beef consumption and switch to a diet based on poultry and vegetables, purchase renewable energy, and install solar panels.
